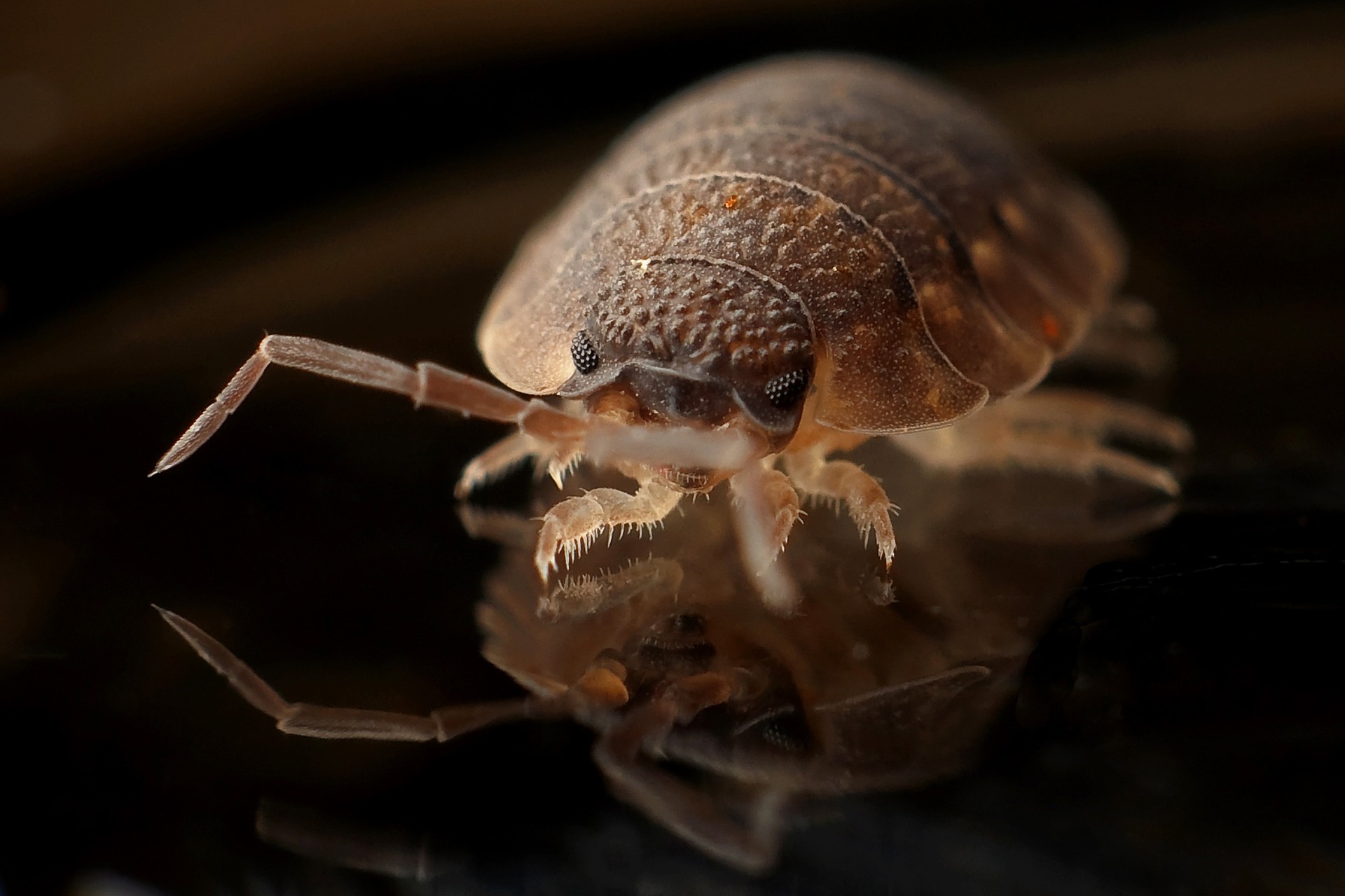
Sowbugs and Pillbugs
- Armadillo-like
- Belong to the same class of animals as lobsters and shrimp
- Need moist conditions to survive
- likes to lie under rocks and debris
- Feed on decaying organic matter
Sowbug Pill bug
-
The sow bugs cannot roll into a tight ball like the pill bug.
-
The sowbug has 2 tail-like appendages that the pill bug does not have.
Millipedes and Centipedes
-
Have many body sections and many legs
House Centipede Millipede
“House” Centipedes: more flattened body compared to the millipede
-
One pair of legs per section
-
Longer legs than millipede
-
Moves more quickly
-
Runs away when disturbed
-
Help to control other insect pests; like to eat spiders, bed bugs, cockroaches, silverfish, carpet beetles, and ants. Therefore can be considered beneficial indoors.
-
Like overly damp areas such as sub-floor, drains, basement, or bathroom
-
Will come indoors in the fall when the weather turns cooler
-
Will hide in cracks, crevices, under the bark of firewood stored indoors, and behind baseboards
Bite: Most are not capable to penetrate human skin. If able, the bite may not cause a reaction to a maximum similar to a mild bee sting. The sting will not cause any serious harm to a cat or dog.
Millipede
-
rounded on top
-
two pairs of legs per section
-
when disturbed, will coil up
Prevention :
-
To reduce moisture retention near your foundation make certain the ground slopes away from your house
-
Remove leaf litter and decaying vegetation around the foundation of your home.
-
Move stones, boards, or boxes away from your foundation (where they tend to hide)
-
Prune and clean around plants near your foundation
-
Allow the soil to dry between waterings.
-
Repair cracks in the foundation and windows.
-
Use a dehumidifier or electric fan to dry damp areas in the basement.
Note: Centipedes, millipedes, sowbugs and pillbugs
- Are not insects but arthropods
- Do not bite, sting, or transmit diseases
- Do not infest food, clothing, or wood
- Are not harmful if found indoors
- Mainly a nuisance
A persistant infestation of sowbugs, pillbugs, or millipedes indoors may indicate a serious moisture problem within your home, and the presence of a food source like rotting wood.
Boxelder bug (Love bugs)
-
Oval-shaped
-
Does not bite humans or spreads disease
-
Deposits eggs on host plant or anywhere they can. Recognized by small red dots
-
Can be found congregating in large masses on the sunny sides of leaves, trees, buildings and rocks
-
Cause minor damage to its preferred host plant by sucking the sap from maple leaves and seed pods causing speckling and distortion of leaf growth
-
Primarily a nuisance
-
Will seek access to warm buildings through any cracks or crevices in foundations, doors, and windows
-
Will search for hibernation sites in the fall to overwinter indoors in dry, sheltered areas; buildings, house attics
Prevention:
-
Repair cracks in foundation, windows and doors to keep them outside
Control:
-
Spray with soap and water when congregated
-
Shake leaves over a pail of water and dish soap
Fleas
-
Parasitic insects
-
Dark brown or reddish brown
-
Have flat bodies
-
Wingless
-
Can jump
-
Peak flea season is August to early October
Bite:
-
Feeds by sucking blood from mammals (humans included) and birds
-
May cause an allergic reaction; rash
-
Can transmit parasites (tapeworm) and diseases like typhus.
-
may cause hair loss due to frequent scratching and biting
-
may cause anemia in extreme cases (severe reduction in red blood cells)
-
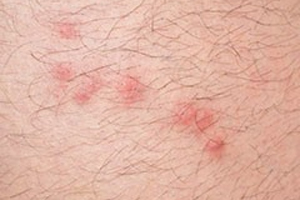
creates a small, hard, red and itchy spot
-is slightly raised and swollen
-has 1 puncture point in the middle
-
Often appear in clusters or lines.
Check your pet for fleas
-
Regularly during flea season and when in contact with other animals
-
Look for black particles the size of ground pepper on your pet’s skin near the tail
-
Inspect sleeping areas, dog houses, kennels for small worm like objects and fleas
Prevention:
-
Inspect your pet regularly
-
Mow and rake your lawn regularly to discourage animals that carry fleas
-
Repair window screens and places unwanted animals my use to enter your home
-
Cover sandbox when not in use
-
Use pest control products made for your pet such as flea collars or spot-on treatments
How to eliminate fleas:
To eliminate fleas you must use a combination of physical and chemical control
On your pet:
- Use a flea comb to remove:
-fleas
-flea feces
-dried blood
Place fleas in hot, soapy water
- And use:
-powders
-shampoos
-foams
In your home:
-
Wash pet and family bedding in hot, soapy water every 2 to 3 weeks.
-
Lift blankets by all 4 corners to avoid scattering the eggs and larvae. If an infestation is severe, replace old pet bedding.
-
Vacuum carpets and cushioned furniture daily.
-
Clean around cracks and crevices on floors and along baseboards.
-
Steam-clean carpets.
Clean:
-
baseboards near sleeping quarters
-
points of entry (for example, around door and window frames)
-
small areas in the yard where pets rest or play (like dog houses)
For more pest control tips:
Sources:














Post a comment